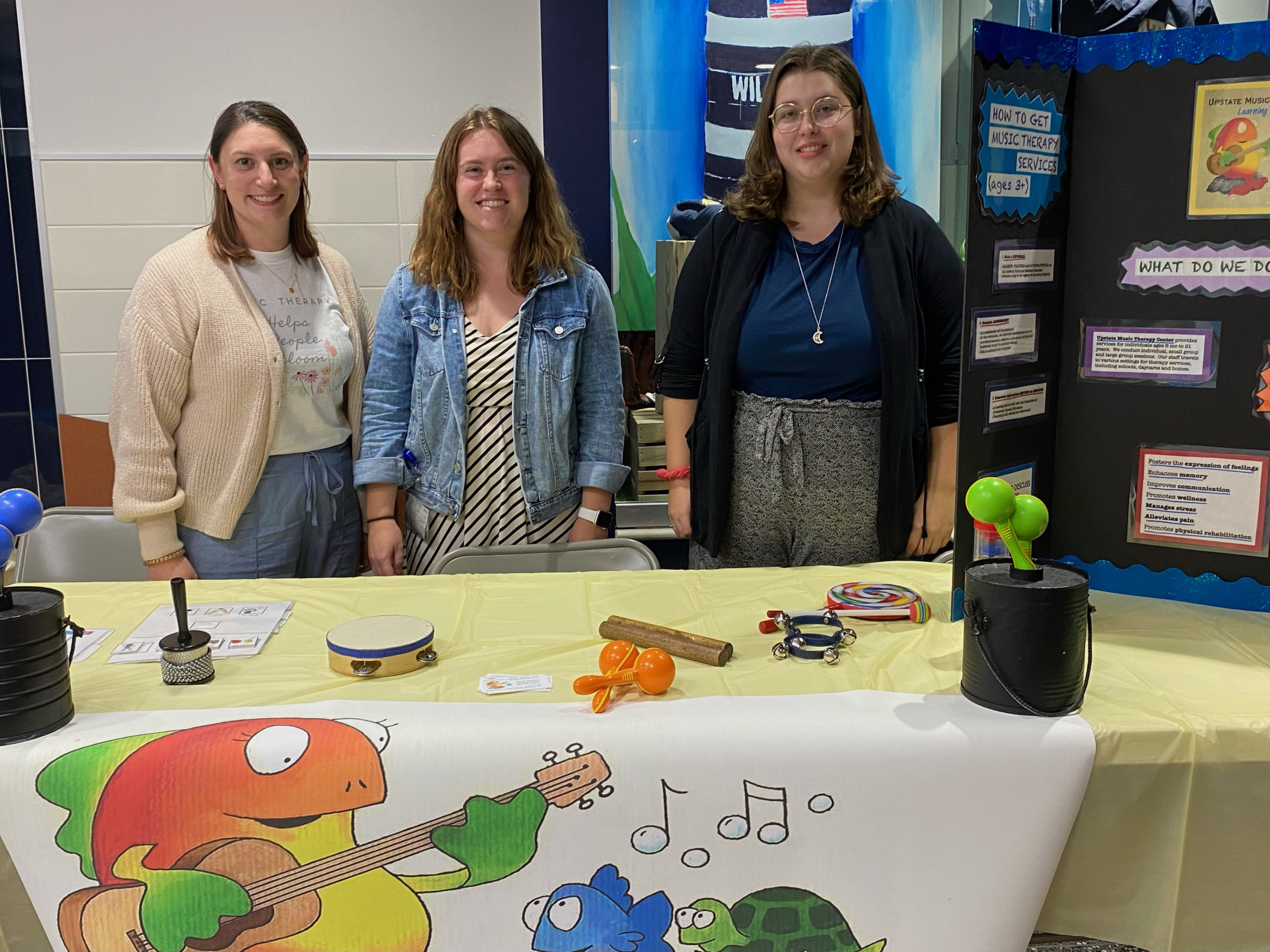
This blog was written by Casey Kunzer, MT-BC On March 1st myself and my colleague Lauren had the opportunity to attend and present at SUNY Fredonia’s Mini Music Therapy Conference. Our presentation, “Becoming MT-BCs,” aimed to educate and empower student music...

Developing Emotional Maturity in Children Using Social-Emotional Learning
Blog post written by Katie Pistilli
If you’re a parent or professional in the education world, you’ve probably noticed a new buzzword: Social-Emotional Learning. What is Social-Emotional Learning, and what does it have to do with public schools?
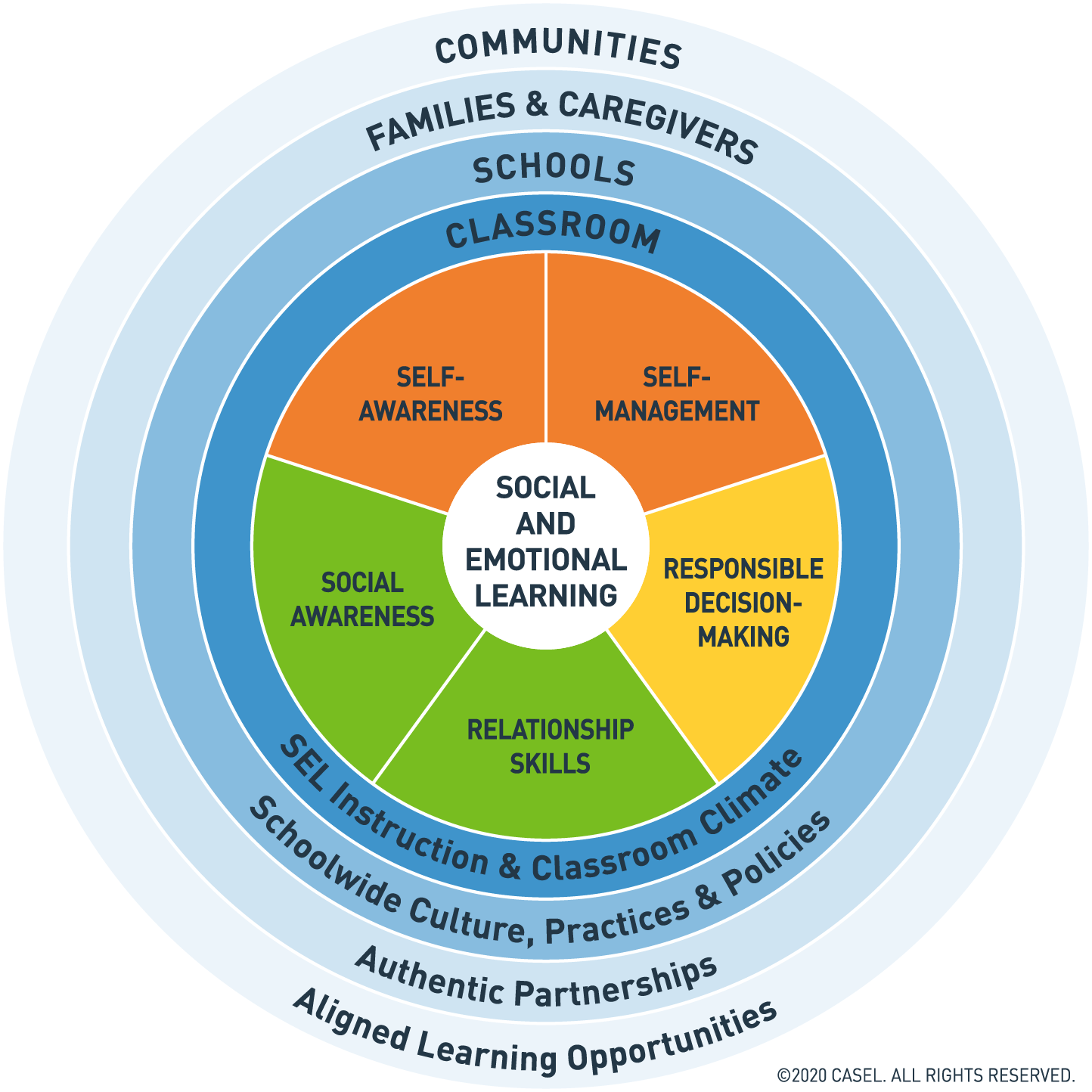
Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) was a term coined by an organization called CASEL, The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning.
According to CASEL, Social-Emotional Learning is “the process through which all young people and adults acquire and apply the knowledge, skills, and attitudes to develop healthy identities, manage emotions and achieve personal and collective goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain supportive relationships, and make responsible and caring decisions.”
SEL guidelines are proven to:
- Increase student’s pro-social skills
- Cultivate skills needed to maintain positive relationships
- Increase academic performance
- Decrease anxiety and depression.
The impact of SEL curriculum spans well into a child’s adulthood, with evidence showing that children exposed to SEL are less likely to experience poverty or incarceration.
SEL is based on the acquisition of 5 core competencies: self-awareness, self-management, responsible decision-making, relationship skills, and social awareness.
A social-emotional learning curriculum not only has an impact on individual students, but their community as a whole.
Music Therapy and Social Emotional Learning
In many ways, music therapists have addressed these benchmarks for decades in our schools. We know the innate social-emotional benefits of making music with others, learning an instrument, and interpreting music. Here are a few specific ways that music therapy addresses the 5 core SEL competencies:
1) Self-Awareness
Self-Awareness ranges from identifying emotions to more complex skills such as linking thoughts to feelings. In music therapy these skills can be addressed with:
- Putting thoughts and feelings to music while songwriting.
- Asking the question: Is this song happy or sad?
2) Self-Management
Self-Management encompasses skills related to managing emotions and coping with stress. In music therapy, we can address these skills with:
- Participating in a drum circle, expressing complex emotions while playing and regulating the body with rhythm.
- Calming the body by breathing in time, using music to slow heart rate, and using mindfulness-based interventions.
3) Responsible Decision-Making
Responsible Decision-Making involves the ability to think critically of one’s actions and how our behavior impacts those around us. In music therapy this might look like:
- Learning how to play instruments and take care of them.
- Listening to peers in a group, being respectful and responding with kindness to their ideas.
4) Relationship Skills
Relationship skills involve social behaviors such as developing friendships and communicating with others. Since music is an innately social experience, it is common to address these skills in music therapy.
- Learning social songs to help children remember and learn the nuances of social behavior such as having conversations or what to do when someone gives a complement.
- Cultivating a hobby or shared interest with a classmate through music.
5) Social Awareness
Social Awareness skills involve understanding the perspectives of others and cultivating empathy. In music therapy this may look like:
- Discussing the meaning behind lyrics and considering what an artist was trying to express.
- Sharing instruments and taking turns during group music making experiences.
The COVID-19 pandemic taught us that now more than ever it is essential to take social-emotional learning seriously. The children in our community have so much to gain from adults in their lives valuing these skills.
If you think music therapy could be a helpful resource for a child you know to work on Social-Emotional Learning skills, please contact us. We would love to hear from you!
Becoming MT-BCs: Presented by Casey Kunzer, MT-BC
World Music Therapy Week 2024
This blog was written by Robin Neary and Amy Thomas. Happy World Music Therapy week! It brings us joy to know that all around the world music therapists are coming together to celebrate and educate our communities on our profession. This year, Upstate Music Therapy...
Current Events: Marcus Whitman Community Partnership Event
This blog post was written by Robin Neary, MT-BC This month, Upstate Music Therapy Center employees Robin Neary, MT-BC, Jamie Swieringa, MT-BC, and Casey Kunzer, MT had the pleasure of attending Marcus Whitman School District’s Community Partnership Event. Families,...